



Next: Polydisperse Systems
Up: Lubrication
Previous: Lubrication
The lubrication forces for 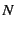 (all) particles
The lubrication forces for
(all) particles
The lubrication forces for 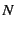 (all) particles
(all) particles
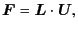 |
(6.1) |
is calculated by
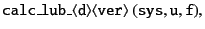 |
(6.2) |
which is called by the top-level function
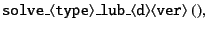 |
(6.3) |
for mobility, resistance, and mixed problems (type)
in 2- and 3-dimensions (d)
with F, FT, and FTS versions (ver).
The function
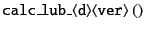 has particle-loops.
Under the periodic boundary condition, particles in the image cells
are also taken into account.
has particle-loops.
Under the periodic boundary condition, particles in the image cells
are also taken into account.
In the loop for particle-particle pairs,
either
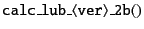 |
(6.4) |
for monodisperse system or
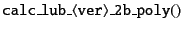 |
(6.5) |
for polydisperse system is called.
Kengo Ichiki 2008-10-12


![]() has particle-loops.
Under the periodic boundary condition, particles in the image cells
are also taken into account.
has particle-loops.
Under the periodic boundary condition, particles in the image cells
are also taken into account.